SEO seems to be getting more and more complex with every year.
Already a bit of a mystery for many site owners, the fact that this field is constantly changing surely doesn’t make things any easier. Trying to stay on top in order to keep your website afloat in the search rankings can result in lots of sleepless nights.
To conquer this feeling of uncertainty, it’s a good idea to take a step back and start from the very beginning.
In the case of search engine optimization, that means looking at what is called technical SEO, which is the basis for search ranking success. While just the word “technical” might be enough to make some people shudder, today we are going to see that it is nothing to fear.
In this article, I will look at technical SEO for WordPress websites, including what it is and how to implement technical SEO measures on your WordPress site.
If you are interested in a closer understanding of this very important topic, just keep reading.
What is Technical SEO For WordPress?
I have already written a number of articles on WordPress SEO right here on Torque:
- WordPress SEO 101: Basics of Search Engine Optimization
- WordPress On-Page SEO: How To Do It Perfectly
- The Best WordPress SEO Plugins And Tools For 2015
- WordPress SEO In Depth: Image Optimization
- SEO in-depth: Understanding and optimizing the WordPress robots.txt
With the exception of the last one, most of them concentrate on optimizing site content.
While that is important (after all, content is king), technical SEO is just as significant since it lays the foundation for any on-page optimization efforts.
It is the scaffolding that holds your content together so that search engines can properly understand and index your website.
Like everything else in this area, technical SEO for WordPress has changed over time. Some things that used to be important in the past are no longer significant today and vice versa.
Since one article is not enough to go over the entire field, I will highlight a number of SEO elements that have become particularly important in recent times. These are:
- Site speed
- Mobile friendliness
- Site architecture
- Other aspects
Are you ready for this? Then let’s get started with speed.
Improve Site Speed For Higher Search Rankings
Page loading time and site speed have become increasingly important in the recent years, especially with the emergence of mobile devices.
Therefore, any technical site optimization should always address this topic.
Why Loading Speed Matters
How quickly a website loads is an important quality measure for both visitors and search engines. A slow site can thus harm you in more than one way.
47% of web users expect a website to load in under two seconds. A full 40% will abandon a site that takes longer than three seconds to open.
Therefore, the slower your site, the higher its abandonment rate.
While just losing visitors is painful enough, a high bounce rate will also signal to Google that your site is of low quality and thus hurt your search rankings.
Sucks, right?
However, it explains why Google has repeatedly stated that page load time is part of their search ranking algorithm, especially for mobile websites.
What they in particular care about is “time to first byte” (TTFB). It means the time it takes for browsers to load the first piece of your website’s data.
TTFB is strongly correlated with search rankings, which is another reason why your site needs to load as fast as possible.
Pinpointing Speed Problems
Many factors can impact how quickly a site loads:
- Quality and location of your hosting provider and server
- HTTP compression and CDN usage
- Implementation of site caching
- Number of active WordPress plugins
- Content optimization, particularly images
However, before you try and throw everything and the kitchen sink at this problem, let’s find out if your site even has a problem, shall we?
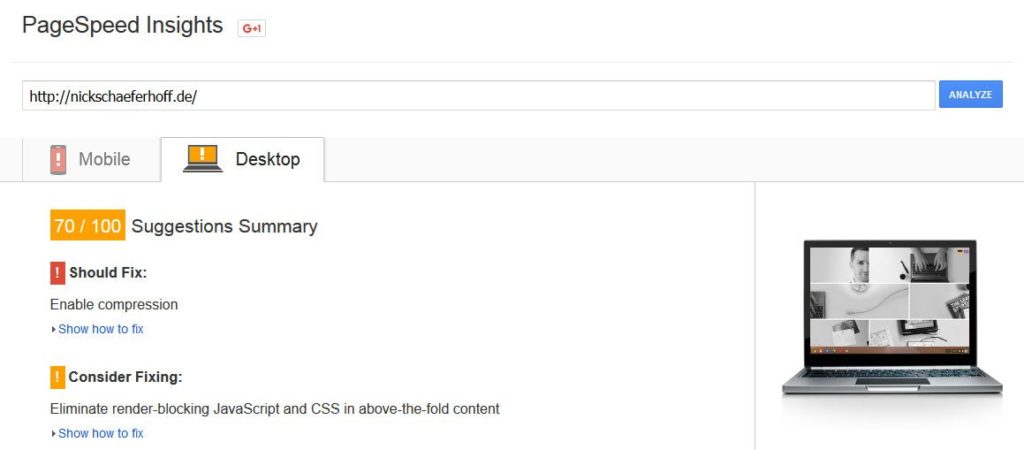
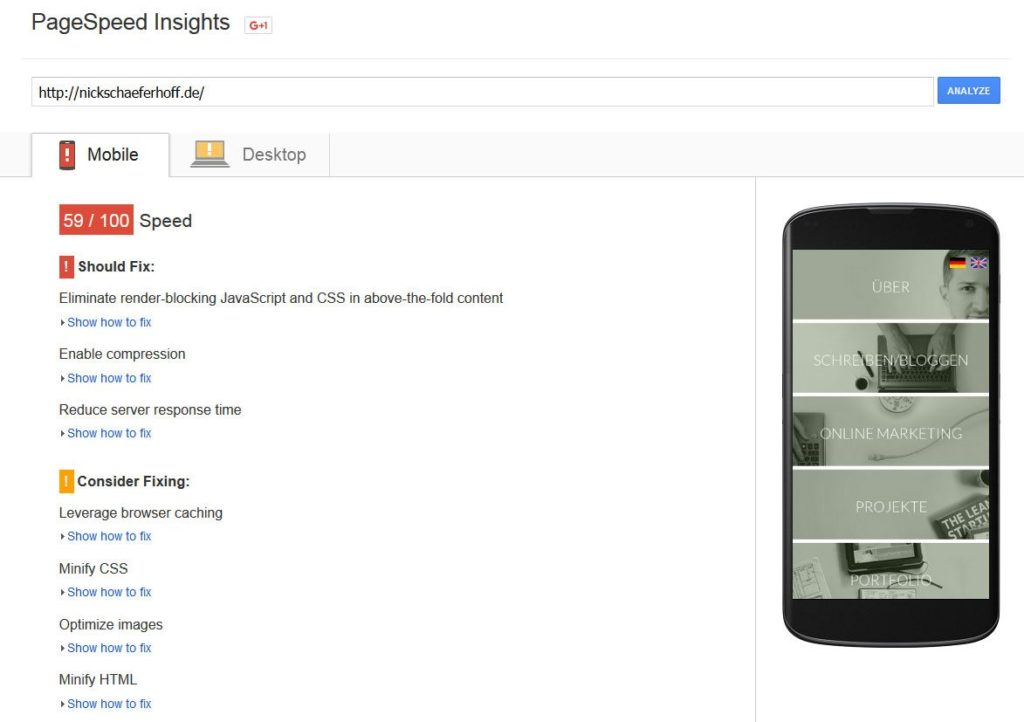
Thankfully, for zoning in on site speed problems Google offers their handy PageSpeed Insights tool.
Just type in your URL, hit Analyze and it will spit out any loading-speed related problems on your site plus recommendation on how to solve them.
Everything shown in red should definitely be addressed. Orange issues are optional but it’s not a bad idea to take care of them as well.
While Google’s tool is usually enough to address the bulk of speed problems, additional tools enable you to dive more deeply into this topic.
GTMetrix and Pingdom offer additional perspectives and can further pinpoint speed issues on your site such as slow server response times.
How To Fix Common Issues
While I can’t go over everything related to site speed issues in this article, here are some basic recommendations:
- Reduce page elements — The less content on a given page, the faster it loads. For that reason, try to keep page elements to a minimum. Besides that, lazy loading for images also helps to reduce initial page load. BJ Lazy Load and Lazy Load are two plugins that can help out here.
- Remove unneeded plugins — Running too many plugins can really do a number on your page load time. Use the Plugins Performance Profiler to pinpoint who is slowing down your site and get rid of them if possible. Apart from that, deactivate plugins that you don’t use permanently.
- Enable caching — Caching means storing a static HTML version of your site on the server instead of having browsers generate it from scratch every time they access your site. A number of excellent plugins can provide this functionality like W3 Total Cache, WP Super Cache and WP Rocket. Some hosts also offer server caching out of the box, so talk to yours about it.
- Optimize images — Visual content often makes up the bulk of page data and should therefore be reduced in size as much as possible. WP Smush can shrink images automatically at upload. You can also use tools like TinyPNG, RIOT and ImageOptim to do the same beforehand. An even better (albeit more complicated method) is to combine images to sprites.
You can do a lot more to decrease your site’s page load time. For an in-depth look at this, check out my article on how to speed up WordPress here on Torque.
Many of the issues mentioned above are also addressed by the Speed Booster Pack, however, I have not yet tested this plugin myself.
Mobile Friendliness – The New Must-Have
Online traffic from mobile devices continues to grow and has in many places surpassed that of desktop computers.
It’s one of the reasons why WordPress 4.4 added native support for responsive images to the platform.
Google also cares about this topic greatly as evidenced by the rollout of their Mobilegeddon update in April last year.
However, that was just the beginning. In the future, we are likely to see more mobile-specific Google updates so you better get your site ready now.
How To Make Your Website Mobile Friendly
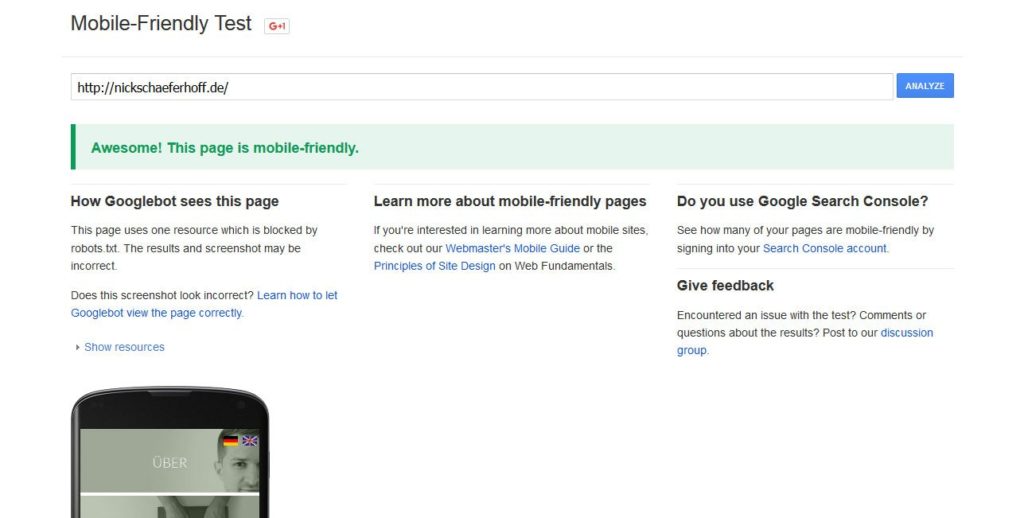
The first address for all things mobile friendliness is Google’s own mobile friendly checker tool.
Inputting your site address and running through its analysis will give you a very good idea whether your site is fit for phones and tablets or not.
In addition to that, if you have Google Webmaster Tools (now Search Console) activated on your site, check under Search Traffic > Mobile Usability for even more info.
For a website to be considered mobile friendly, two main aspects are important:
- A mobile-friendly design
- Page load time on mobile
The first part can be achieved in two main ways:
- Responsive design — The website layout automatically adjusts to the size of the screen.
- Alternative site versions — A dedicated mobile site version is available and visitors are redirected according to their type of device.
The first method is preferred. All high-quality themes should by now work seamlessly on mobile as well as desktop devices.
If yours doesn’t, I recommend either changing it or making it responsive. Just make sure it looks as good on tablets and phones as it does on desktop computers.
Finally, we also have a number of plugins which can help optimize your site for mobile traffic and you can find a lot of them in this article.
Concerning mobile loading speed, follow the same steps mentioned above for general speed optimization. Google also has a dedicated section for mobile loading speed in their tool.
Optimize Site Architecture For SEO
A clear and simple site structure helps websites get indexed by search engines more easily. That’s nothing new but an important part of technical SEO and therefore bears repeating.
Create A Logical Information Hierarchy
Just like human visitors, Google uses the way site content is order to figure out what a website is about.
A clear and concise site structure is, therefore, important not only for user experience and user guidance but also search engine optimization.
WordPress does a lot of organization out of the box by using taxonomies.
By creating main and subcategories, you can set up a clear and understandable order for both human beings and machines.
When a search spider lands on a category archive, it can understand that all content on this page belongs to the same topic and what that topic is.
However, don’t overdo it! If you have too many categories, it can make your site look disorganized, dilute your topic, and do much more harm than good.
Eliminate Crawl Errors And Set Redirects
Crawl errors are pages that cannot be found or accessed and thus produce the dreaded 404 error.
While you can create a custom 404 page to help visitors find what they are looking for, a better idea is to get rid of missing pages altogether.
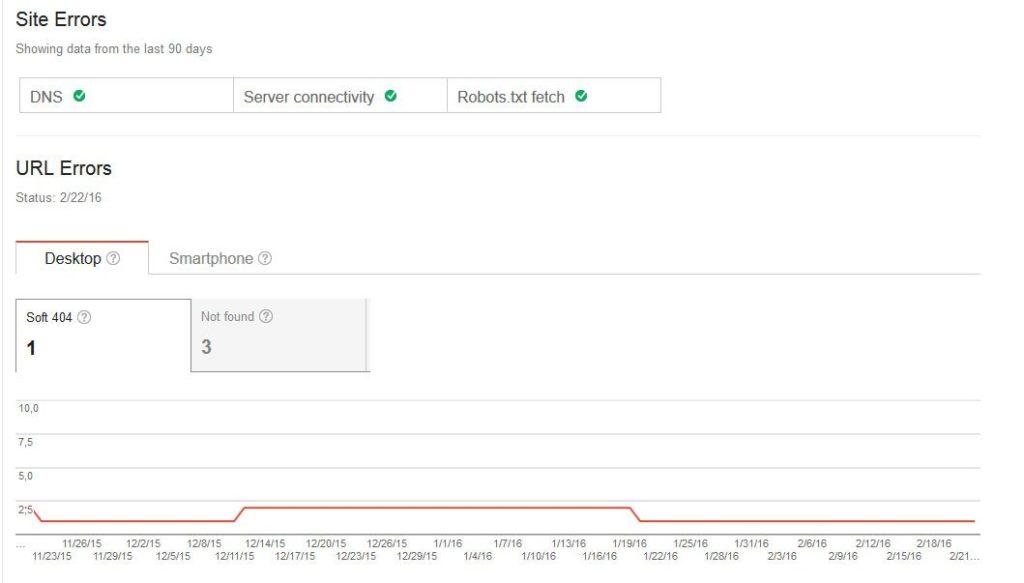
To get an impression on how accessible your site content is, check Crawl > Crawl Errors in Google’s Search Console.
If your site is throwing a lot of red flags here, Moz has an excellent guide on how to fix crawl errors on websites.
However, one solution that bears mentioning are page redirects.
Redirects enable you to tell search engines when content has moved to another URL or point them to a different place when a page no longer exists.
They also help retain visitors that get to your site from a faulty link by sending them somewhere relevant instead of a 404 error page.
However, when you do set up redirects, it’s important to use 301 redirects, not 302.
The latter only signifies a temporary move and will therefore not transfer any existing link juice to the new page.
The best way to implement this in WordPress is the Redirection plugin.
It makes creating redirects super easy and will also track when someone lands on a 404 error page so you can send visitors to the right place in the future.
Highly recommended!
Rid Yourself Of Duplicate Content
Google’s Panda update specifically targeted low-quality content. That includes duplicate content which visitors don’t like it and neither do search engines.
The problem is that WordPress automatically creates lots of it, e.g. in the form of author and date archives which often contain the same articles as the main blog loop.
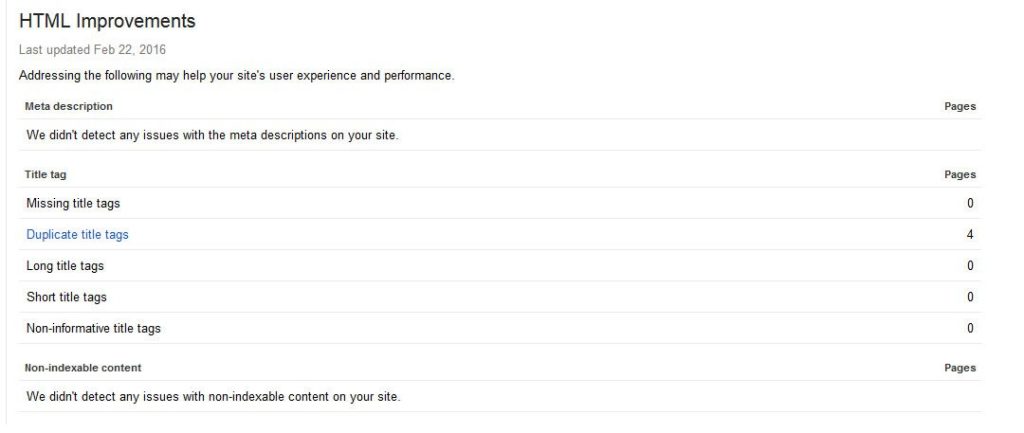
If you haven’t configured your site correctly, this could become an issue. To find out if it already is, check your Google Search Console under Search appearance > HTML improvements.
Any problems with duplicate titles, meta descriptions, and other issues will show up here. You can even click on each link to see which pages in particular are in need of remedial action.
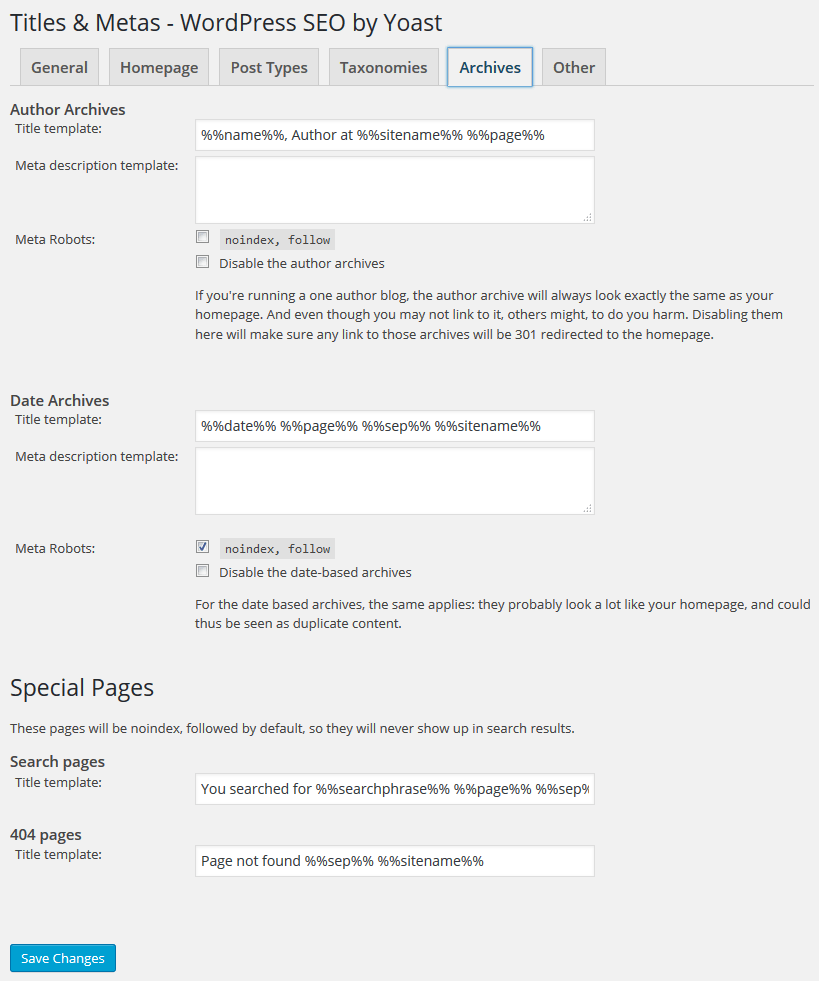
One of the easiest solutions to address duplicate content is using Yoast SEO.
The plugin enables you to set noindex, follow meta tags for different types of content. That means search engines will follow the link but refrain from adding the content of that page to the Google library.
This setting can be used to reduce the amount of duplicate content on WordPress websites and is easier to implement than manual measures.
For more detailed explanations on this topic, check my in-depth guide to Yoast SEO.
Other Aspects of Technical SEO for WordPress
Below are two more things that didn’t fit the above categories but fall under technical SEO: Sitemaps and structured data. Both of them are important so pay attention until the end.
Create a Sitemap
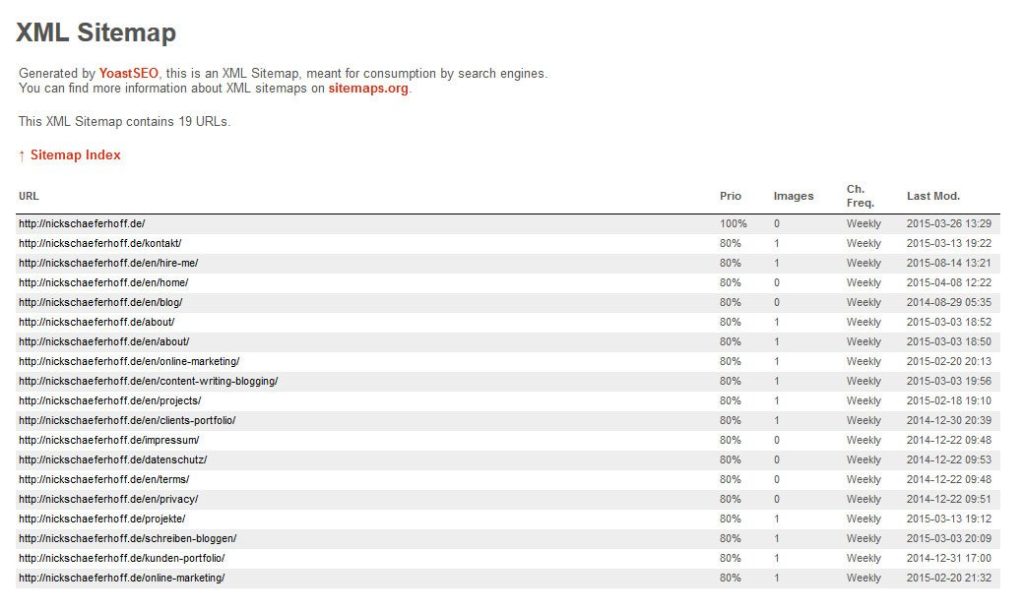
A sitemap is basically a list of all URLs on your site. It looks like this:
Sitemaps can be set up in two forms: HTML and XML.
HTML versions are usually meant for humans and often found in the footer of websites. Search spiders can use them as well, but it’s not their primary goal.
On the other hand, an XML sitemap is a simple text file that maps the entire content of your website purely for machine consumption.
Besides providing a roadmap of your site, they also often include information on how content is prioritized and how often search engines should check back for more.
XML Sitemaps can also be submitted directly to Google and other search engines. So, instead of hoping for them to find you and index your content, you can tell them exactly what your site has to offer.
The easiest way to create an XML sitemap is via a plugin like Google XML Sitemaps or the aforementioned Yoast SEO, which also has this functionality included.
When you have done so, don’t forget to submit it to Google under Crawl > Sitemaps (use the Add/Test button).
While you are at it, also add the sitemap to your robots.txt file so search spiders who come by your site can find it.
It’s as easy as adding the following lines (with updated URLs, of course) to your site’s robots.txt.
Sitemap: http://yoursite.com/sitemap1.xml Sitemap: http://yoursite.com/sitemap2.xml
Use Structured Data
While search engines are getting better at understanding different elements on web pages, structured data markup can help them even further.
Structured data is nothing but meta tags that describe the content to search engines who can then use it to create rich snippets including pictures, ratings and more.
The most commonly used markup is Schema.org. While some themes have Schema support built in, we can also use something All In One Schema.org Rich Snippets to add the markup to our website.
The plugin supports reviews, events, people, products, recipes, videos, articles, and more.
After you have added structured data to your site, don’t forget to check if it works properly with Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool.
Technical SEO Doesn’t Have To Be Complicated
Like SEO in general, technical SEO for WordPress can be an intimidating topic which is why many people shy away from it.
However, since the technical side forms the foundation for any content optimization, it shouldn’t be ignored.
The article above has shown you some of the most important aspects of technical SEO and how to put them into practice within WordPress.
The important thing to understand is that like everything in web publishing, technical SEO for WordPress is nothing mysterious but something that can be understood and learned.
Plus, we have loads of free, high-quality tools at our disposal to make implementation as easy as possible. Also, you don’t have to do everything at once. Just picking one or two items from the list and putting them into action already puts you ahead of the curve.
How do you implement technical SEO on your WordPress site? Anything to add to the above, questions or things you need help with? Let us know in the comments!


2 Comments